Introduction:
Blending and juicing have gained popularity as convenient ways to incorporate more fruits and vegetables into our diets. These methods offer different approaches to consuming nutrient-rich produce. In this article, we will explore the benefits of blending and juicing, helping you understand which method might suit your preferences and nutritional goals.
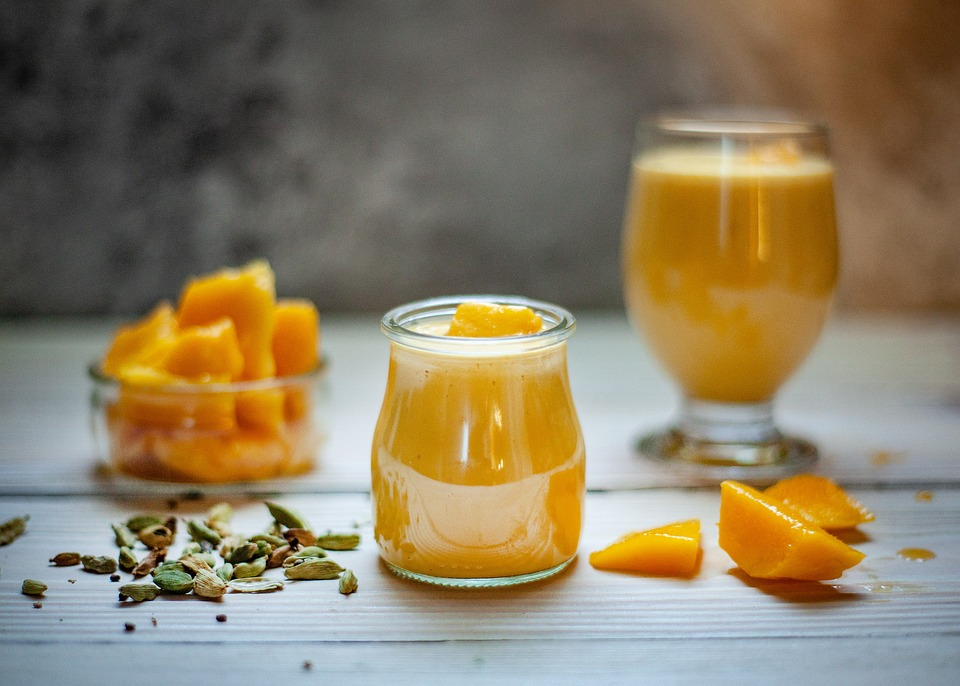
Blending:
Blending involves blending whole fruits and vegetables into a smoothie-like consistency, retaining the fiber content along with the juice.
1. Fiber Powerhouse:
One of the significant advantages of blending is that it retains the dietary fiber present in fruits and vegetables. Fiber aids in digestion, promotes feelings of fullness, and supports a healthy gut. Blended drinks provide a more satiating effect, potentially helping with weight management and blood sugar control.
2. Nutrient Retention:
Blending preserves the majority of the nutrients found in fruits and vegetables, including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. The blending process breaks down the cell walls, making it easier for the body to absorb and utilize these nutrients effectively.
Juicing:
Juicing involves extracting the liquid content from fruits and vegetables, leaving behind the fiber.
1. Increased Nutrient Absorption:
Juicing allows for the quick absorption of nutrients as the fiber is removed. The nutrients are readily available to the body without the need for extensive digestion. This can be beneficial for individuals with compromised digestion or those seeking a quick nutrient boost.
2. Concentrated Nutrient Intake:
Juicing enables the consumption of a larger volume of fruits and vegetables in a condensed form. This can be especially advantageous for individuals who struggle to consume sufficient amounts of produce in their whole form. Juices provide a concentrated dose of vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients.
Conclusion:
Both blending and juicing offer unique benefits, and the choice between the two depends on personal preferences, dietary needs, and health goals. Blending retains the fiber content, providing a satisfying and well-rounded nutritional beverage. On the other hand, juicing offers quick nutrient absorption and concentrated nutrient intake. Incorporating both methods into your routine can be a well-rounded approach to boost your fruit and vegetable intake.
References:
1. Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health - The Nutrition Source: Fiber: https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/carbohydrates/fiber/
2. Mayo Clinic - Juicing: What Are the Health Benefits?: https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/expert-answers/juicing/faq-20058020
3. National Institutes of Health - Dietary Fiber: Essential for a Healthy Diet: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3614039/
4. Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics - Juicing: What You Need to Know: https://www.eatright.org/food/vitamins-and-supplements/nutrient-rich-foods/juicing-what-you-need-to-know