Introduction:
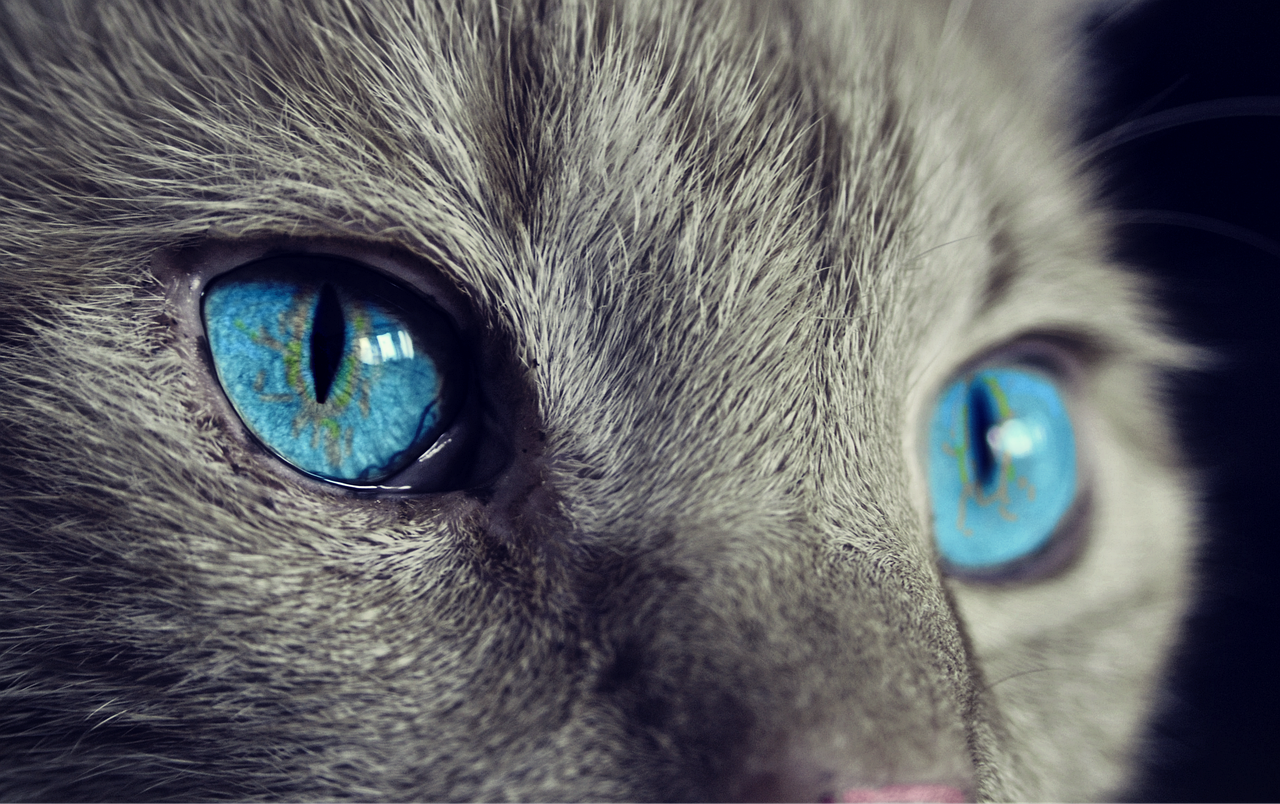
Cats are known for their exceptional vision, especially in low-light conditions. Their ability to navigate and hunt in the dark has fascinated humans for centuries. But can cats truly see better than us in the dark? In this article, we delve into the fascinating world of feline vision to understand how cats' eyes are adapted for low-light environments and explore the truth behind their superior night vision.
1. Night Vision Adaptations:
Cats possess several adaptations that enhance their vision in low-light conditions. One crucial feature is their large pupils, which allow more light to enter their eyes. Additionally, cats have a layer of cells called the tapetum lucidum located behind the retina. This reflective layer bounces incoming light back through the retina, maximizing its sensitivity and improving their ability to capture and amplify available light.
2. Specialized Retinal Cells:
Another factor contributing to cats' superior night vision is the presence of specialized retinal cells called rods. These cells are highly sensitive to light and play a crucial role in detecting motion and objects in dimly lit environments. Cats have a higher density of rods in their retinas compared to humans, allowing them to detect even the slightest movements in the dark.
3. Enhanced Visual Acuity:
Cats' eyes also possess a higher concentration of rod cells around the central portion of their retinas, known as the fovea. This concentration enhances their visual acuity and ability to focus on small details, even in low-light conditions. Combined with their excellent depth perception, this feature enables cats to accurately judge distances and pounce on prey with precision, even in near darkness.
4. Adaptations for Hunting:
Cats' superior night vision is closely linked to their natural hunting instincts. In the wild, cats are crepuscular animals, meaning they are most active during dawn and dusk when lighting conditions are challenging. Their exceptional night vision allows them to stalk and capture prey effectively during these periods. Domestic cats, although adapted to a more diurnal lifestyle, still retain many of these visual advantages.
Conclusion:
It is true that cats possess remarkable visual adaptations that allow them to see better than us in the dark. Their large pupils, the presence of the tapetum lucidum, specialized retinal cells, and enhanced visual acuity all contribute to their superior night vision capabilities. These adaptations are an integral part of their evolutionary history as nocturnal and crepuscular hunters. So, the next time you witness your cat effortlessly navigating a dark room, remember that their remarkable vision is one of nature's marvels.
References:
1. Live Science. (2021). Why Can Cats See in the Dark? Retrieved from https://www.livescience.com/34317-cats-eyes-night-vision.html
2. Animal Planet. (n.d.). Cats Can See in the Dark. Retrieved from https://www.animalplanet.com/pets/cats-can-see-in-the-dark
3. VCA Animal Hospitals. (n.d.). Night Vision and Cats. Retrieved from https://vcahospitals.com/know-your-pet/night-vision-and-cats
4. National Geographic. (2019). How Do Cats See in the Dark? Retrieved from https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/article/how-do-cats-see-in-the-dark