Introduction:
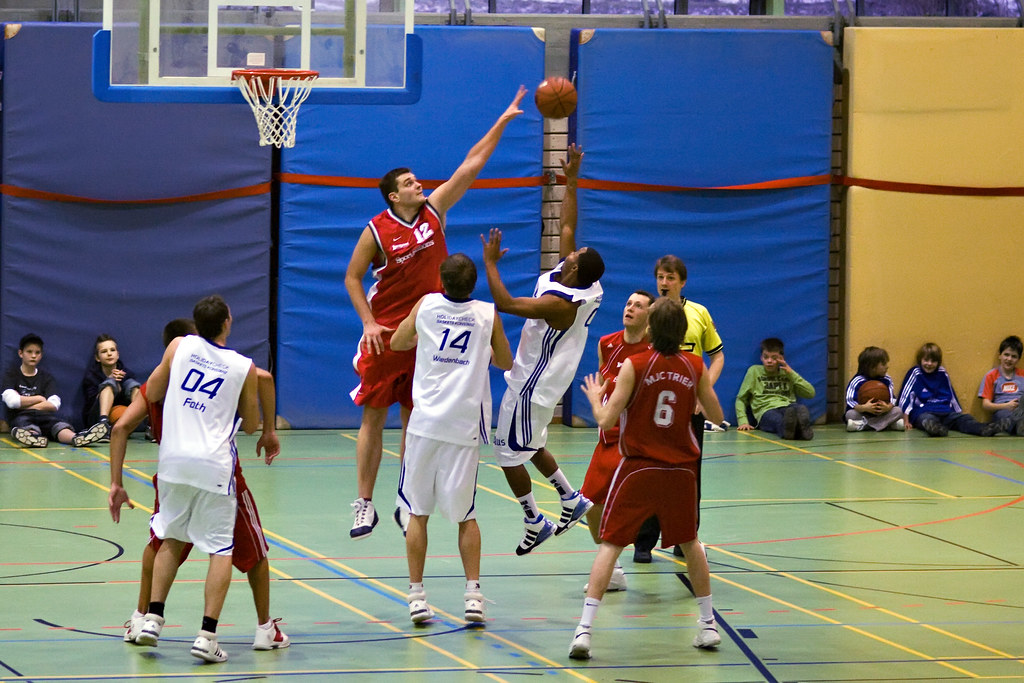
Basketball, a sport loved by millions around the world, is known for its fast-paced action and competitive nature. Beyond its entertainment value, basketball offers numerous physical and mental benefits. One significant advantage is its positive impact on coordination skills. The game requires players to exhibit exceptional hand-eye coordination, footwork, balance, agility, and spatial awareness. In this article, we will explore how basketball promotes coordination and discuss the various advantages it brings.
1. Hand-Eye Coordination:
Basketball demands superior hand-eye coordination as players need to dribble, shoot, and pass the ball accurately while maintaining awareness of their surroundings. The ability to control the ball while navigating the court, making split-second decisions, and executing precise movements sharpens hand-eye coordination. Regular basketball practice hones this essential skill, leading to improved motor control and precision in various activities.
2. Footwork and Balance:
Basketball places significant emphasis on footwork and balance. Players must move swiftly and efficiently on the court, change directions rapidly, and maintain balance while executing moves such as pivots, jumps, and cuts. The constant coordination between foot movements and overall body control enhances foot-eye coordination and improves balance, contributing to better overall coordination skills.
3. Agility and Quickness:
Basketball is a sport that requires quick reactions and rapid movements. Players must be agile and explosive, capable of accelerating, decelerating, and changing direction swiftly. The continuous changes in speed and direction, combined with the need for quick reflexes, enhance agility and quickness. The development of these attributes directly impacts coordination, allowing players to navigate the court effectively and make coordinated movements.
4. Spatial Awareness:
Basketball demands excellent spatial awareness, as players must be aware of their positioning on the court, judge distances accurately, and make split-second decisions. This includes understanding the position of teammates and opponents, finding open passing lanes, and executing precise shots. The development of spatial awareness in basketball translates to improved coordination and decision-making skills in various contexts.
5. Motor Skills and Reaction Time:
Basketball requires players to execute various motor skills such as shooting, dribbling, and passing, often in high-pressure situations. The repetitive practice of these skills enhances motor coordination and fine-tunes muscle memory. Additionally, the rapid decision-making and quick reactions necessary during gameplay improve reaction time, further honing overall coordination skills.
Conclusion:
Basketball is more than just a sport; it is a platform for enhancing coordination skills. The focus on hand-eye coordination, footwork, balance, agility, spatial awareness, motor skills, and reaction time in basketball leads to improved overall coordination. Engaging in regular basketball practice not only enhances motor control and agility but also develops crucial cognitive abilities such as decision-making and spatial awareness. The benefits of basketball extend beyond the court, impacting various aspects of life that require coordination and adaptability. Check out other sports that require exceptional hand-eye coordination.
References:
1. Davids, K., Button, C., & Bennett, S. (2008). Dynamics of skill acquisition: A constraints-led approach. Human Kinetics.
2. Hughes, M., & Bartlett, R. (2002). The use of video and integrated computer graphics to develop decision-making skills in team games. Journal of Sports Sciences, 20(10), 873-888.
3. Leite, N. J., Gomide, E. B., & Baptista, R. R. (2011). Coordination motor skills in Brazilian basketball players from different competitive levels. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 112(1), 129-144.
4. Malina, R. M., & Bouchard, C. (2004). Growth, maturation, and physical activity. Human Kinetics.