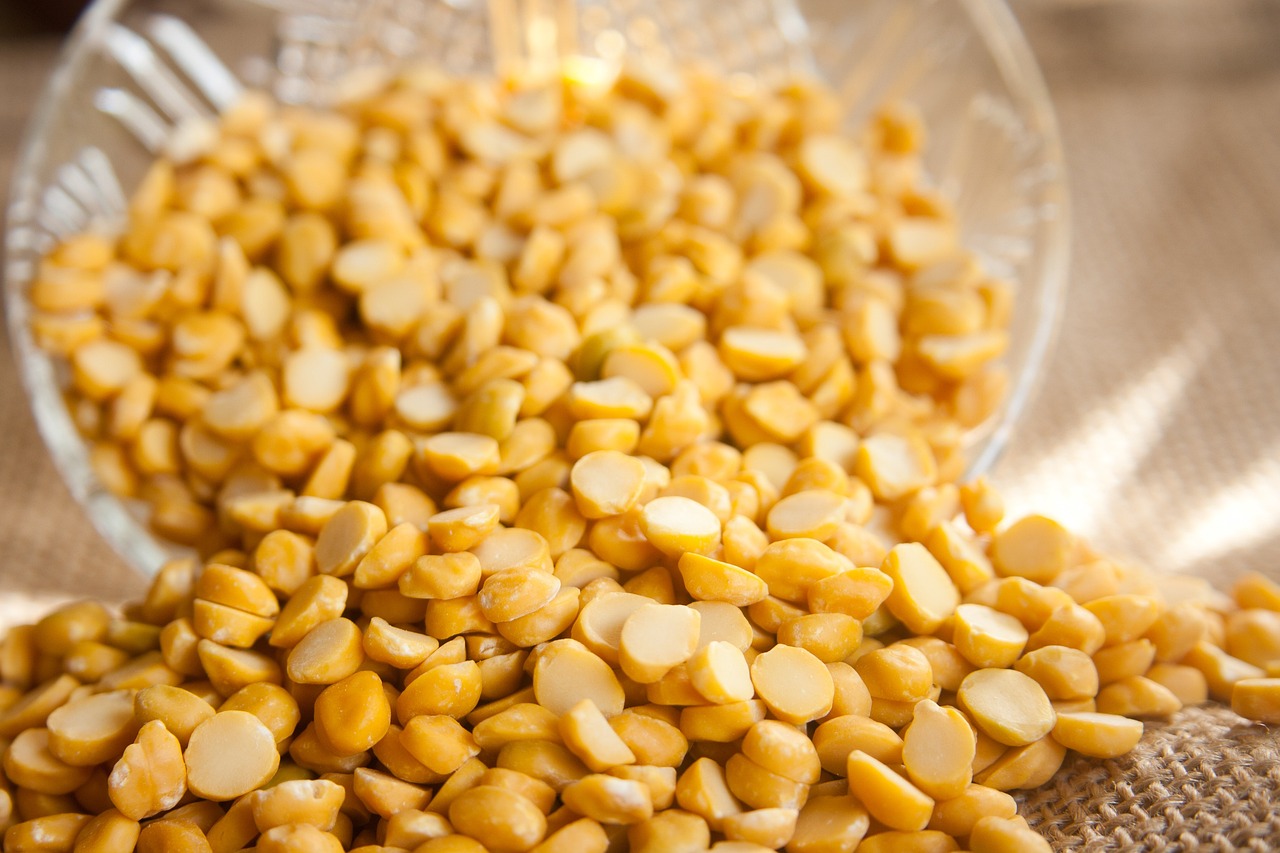
Dal, also known as lentils or pulses, holds a significant place in the culinary traditions of many cultures around the world. These edible seeds are not only versatile and delicious, but they also provide a host of health benefits. From providing essential nutrients to promoting heart health, dal is a powerhouse of nutrition. In this article, we will explore what dal is, delve into five types of dal, and uncover their unique health benefits.
What is Dal?
Dal refers to dried, split pulses that come from various legume plants. These legumes are harvested and then processed to remove the outer husk, leaving the inner seed or dal. The dal is then split into halves or even smaller pieces for cooking. Commonly consumed in South Asia, dal is a staple in Indian cuisine and is enjoyed in a variety of dishes, including soups, stews, curries, and side dishes.
Types of Dal and Their Benefits:
1. Masoor Dal (Red Lentils):
Masoor dal is one of the most commonly consumed lentils, known for its distinct red color. Rich in dietary fiber, folate, iron, and protein, masoor dal aids in digestion, promotes heart health, and boosts energy levels. It is also an excellent source of antioxidants, helping to combat oxidative stress and inflammation.
2. Moong Dal (Mung Beans):
Moong dal, also known as mung beans, is a versatile and easily digestible dal variety. It is a great source of plant-based protein, dietary fiber, and essential minerals such as potassium and magnesium. Moong dal promotes healthy digestion, regulates blood sugar levels, and contributes to weight management. Additionally, it is beneficial for skin health due to its detoxifying properties.
3. Toor Dal (Pigeon Peas):
Toor dal, commonly known as arhar dal or split pigeon peas, is widely used in Indian cuisine. It is a rich source of dietary fiber, plant-based protein, vitamins, and minerals. Toor dal aids in managing cholesterol levels, supports bone health, and provides a sustainable release of energy. Moreover, it contains essential amino acids, making it a valuable protein source for vegetarians and vegans.
4. Chana Dal (Split Bengal Gram):
Chana dal, derived from split Bengal gram, is a nutrient-dense dal variety. It is packed with protein, dietary fiber, folate, iron, and manganese. Chana dal aids in weight management, promotes digestion, and helps control blood sugar levels. Additionally, it offers satiety, making it an excellent choice for those aiming to reduce their calorie intake.
5. Urad Dal (Black Gram):
Urad dal, also known as black gram, is a highly prized dal variety in Indian cuisine. It is rich in plant-based protein, dietary fiber, iron, magnesium, and potassium. Urad dal aids in improving digestion, boosts energy levels, and contributes to maintaining healthy skin and hair. It is often used to prepare traditional dishes like dosa and idli.
Conclusion:
Dal, with its incredible versatility and nutritional benefits, is a true gift of nature. Whether you prefer masoor dal, moong dal, toor dal, chana dal, or urad dal, incorporating these lentils into your diet can provide a range of health benefits. From supporting digestion to promoting heart health and providing essential nutrients, dal is a valuable addition to a balanced and nutritious diet.