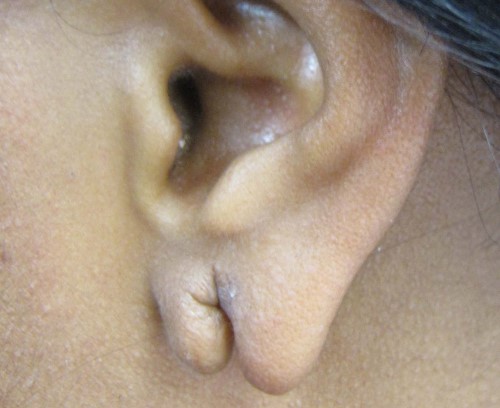
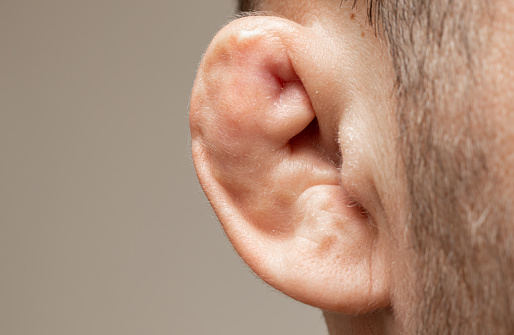
Torn earlobes can be an unwelcome and distressing occurrence, affecting individuals who wear earrings or have experienced trauma to their earlobes. Whether due to accidental pulling, heavy earrings, or gauging, these injuries can significantly impact a person's appearance and self-confidence. In this article, we explore the causes of torn earlobes and delve into common techniques used for their repair.
Causes of Torn Earlobes:
1. Trauma and Accidental Pulling:
Sudden forceful pulling or trauma to the earlobe, often caused by getting earrings caught on clothing or other objects, can result in a torn earlobe. This is particularly common when earrings are excessively heavy or snagged unexpectedly.
2. Heavy Earrings:
Prolonged or frequent wear of heavy earrings can strain the earlobe, leading to stretching and eventually tearing. The weight of the earrings can pull down on the earlobe, causing the tissues to become thin and susceptible to tearing.
3. Gauging or Earlobe Stretching:
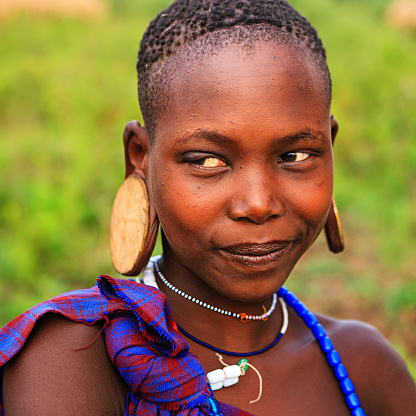

Gauging involves intentionally stretching the earlobe by gradually increasing the size of earlobe piercings. If done improperly or too quickly, it can result in the thinning and tearing of the earlobe tissue. This is common in some African countries.
Repairing Torn Earlobes:
1. Surgical Repair:
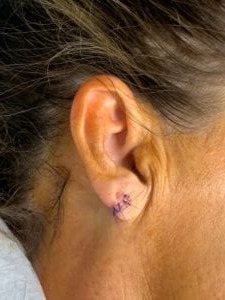
The most common and effective method for repairing torn earlobes is a surgical procedure known as earlobe repair or earlobe reconstruction. This procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia on an outpatient basis. The surgeon carefully removes any damaged or excess tissue, aligns the edges of the tear, and then sutures them back together, creating a neat and well-healed earlobe.
2. Lobe Reconstruction with Flaps:
In cases where the tear is significant or the earlobe tissue is severely damaged, a technique called lobe reconstruction with flaps may be employed. This technique involves using adjacent healthy tissue to cover the tear and rebuild the earlobe. It provides additional support and strength to the repaired area.
3. Tissue Adhesives:
For minor tears or as a temporary solution until a surgical repair can be performed, tissue adhesives may be used. These medical-grade adhesives are applied to the edges of the tear, holding them together while the earlobe heals. However, it's important to note that tissue adhesives are not a permanent solution and may not be suitable for all types of tears.
Conclusion:
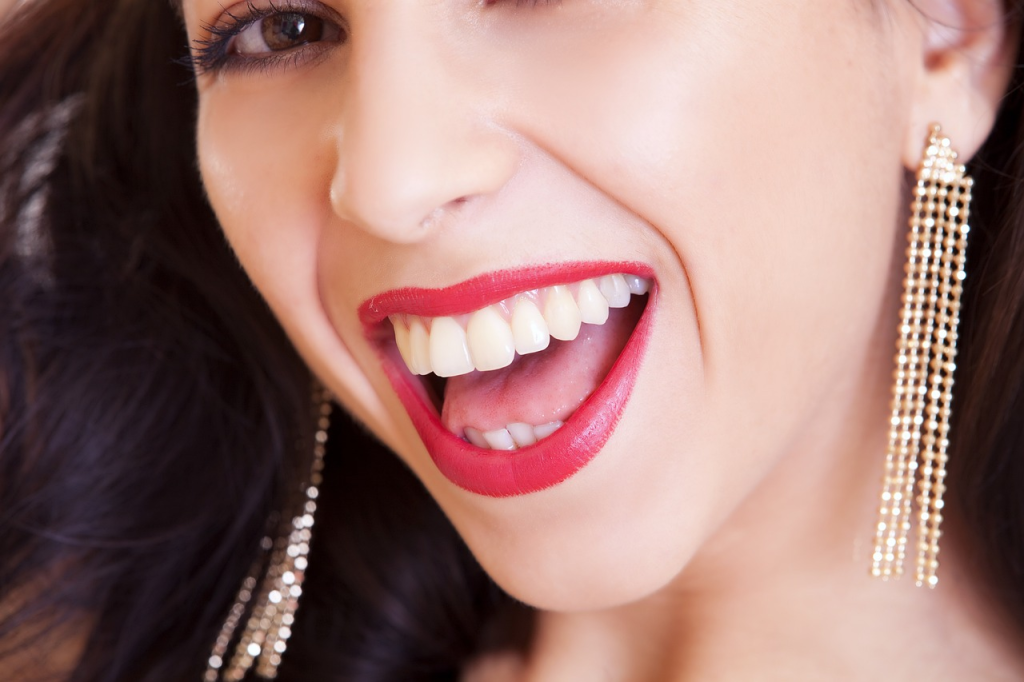

Torn earlobes can be caused by trauma, heavy earrings, or gauging. Fortunately, there are effective techniques available for repairing these injuries. Surgical repair, often performed under local anesthesia, is the most common approach, involving the careful alignment and suturing of the torn earlobe tissue. In more complex cases, lobe reconstruction with flaps may be necessary. For minor tears, temporary solutions such as tissue adhesives can be used until a surgical repair is performed. If you experience a torn earlobe, consulting with a qualified healthcare professional or plastic surgeon will help determine the most appropriate course of action.
References:
1. American Society of Plastic Surgeons. (2019). Earlobe Repair.
https://www.plasticsurgery.org/reconstructive-procedures/earlobe-repair
2. Mayo Clinic. (2021). Earlobe Repair.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/earlobe-repair/about/pac-20385068
3. American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. (2014). Torn Earlobe Repair.