Introduction:
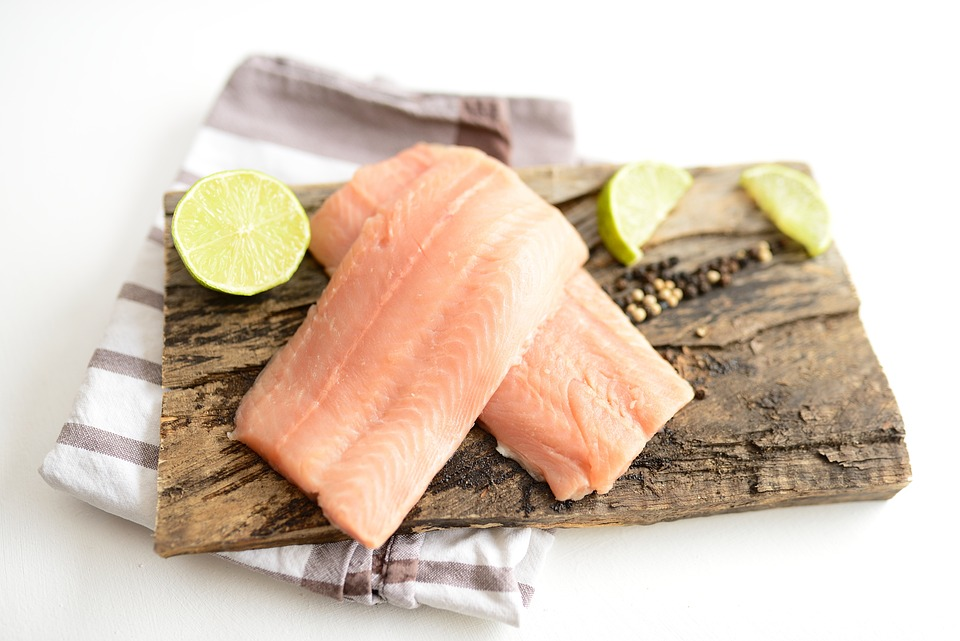
Salmon is a popular fish known for its nutritional value and delicious taste. However, not all salmon is created equal. There are significant differences between wild-caught salmon and farmed salmon, ranging from their habitat and diet to their nutritional content. In this article, we will explore the disparities between wild salmon and farmed salmon, and discuss why wild salmon is often considered the healthier choice.
1. Habitat and Lifestyle:
Wild Salmon:
Wild salmon are born and raised in natural environments such as rivers and oceans. They spend their lives swimming freely in the open waters, which allows them to develop a leaner and more muscular body. Their natural habitat and active lifestyle contribute to their distinct flavor and texture.
Farmed Salmon:
Farmed salmon, as the name suggests, are raised in captivity within net pens or enclosed areas. These environments are often overcrowded, restricting the fish's movement. Farmed salmon are typically fed a controlled diet to promote rapid growth, leading to a higher fat content.
2. Diet and Nutrition:
Wild Salmon:
Wild salmon feed on a diverse diet consisting of smaller fish, krill, and other natural organisms found in their habitat. This varied diet contributes to their higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for heart and brain health. Wild salmon also contain lower levels of unhealthy saturated fats.
Farmed Salmon:
Farmed salmon are typically fed a diet that includes a combination of fishmeal, fish oil, and plant-based ingredients. This diet can result in lower levels of omega-3 fatty acids compared to wild salmon. Farmed salmon may also contain higher levels of unhealthy fats, including saturated fats.
3. Contaminant Levels:
Wild Salmon:
Due to their natural diet and environment, wild salmon generally have lower levels of contaminants such as polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and dioxins. These pollutants can accumulate in fish through their food chain. However, it's worth noting that the overall levels of contaminants in wild salmon are still considered to be within safe limits.
Farmed Salmon:
Farmed salmon are more susceptible to contamination due to their confined environment and controlled diet. The feed they consume may contain contaminants, which can accumulate in their flesh. Although farmed salmon undergo testing and regulations to ensure safety, their levels of contaminants may be slightly higher compared to wild salmon.
Conclusion:
When comparing wild salmon and farmed salmon, it is clear that wild salmon has several advantages from a health perspective. Wild salmon's natural habitat, diverse diet, and active lifestyle contribute to its leaner body, higher omega-3 fatty acid content, and lower levels of contaminants. While farmed salmon can still be a source of nutrients, its confined environment and controlled diet may result in a higher fat content and lower omega-3 levels. When choosing salmon, opting for wild-caught varieties can provide a healthier and more nutritious option.
References:
1. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) - Wild-Caught Salmon vs. Farmed Salmon: https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/feature-story/wild-caught-salmon-vs-farmed-salmon
2. American Heart Association - Fish and Omega-3 Fatty Acids: https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/fats/fish-and-omega-3-fatty-acids
3. Environmental Defense Fund - Seafood Selector: Farmed Salmon: https://www.edf.org/seafood/farmed-salmon
4. Mayo Clinic - Omega-3 in Fish: How Eating Fish Helps Your Heart: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heart-disease/in-depth/omega-3/art-20045614
5. Monterey Bay Aquarium Seafood Watch - Salmon Recommendations: https://www.seafoodwatch.org/seafood-recommendations/groups/salmon?q=salmon